NASA Headquarters
 Washington, D.C. – An evocative new image sequence from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft offers a departing view of the Kuiper Belt object (KBO) nicknamed Ultima Thule – the target of its New Year’s 2019 flyby and the most distant world ever explored.
Washington, D.C. – An evocative new image sequence from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft offers a departing view of the Kuiper Belt object (KBO) nicknamed Ultima Thule – the target of its New Year’s 2019 flyby and the most distant world ever explored.
These aren’t the last Ultima Thule images New Horizons will send back to Earth – in fact, many more are to come — but they are the final views New Horizons captured of the KBO (officially named 2014 MU69) as it raced away at over 31,000 miles per hour (50,000 kilometers per hour) on January 1st. The images were taken nearly 10 minutes after New Horizons crossed its closest approach point.
“This really is an incredible image sequence, taken by a spacecraft exploring a small world four billion miles away from Earth,” said mission Principal Investigator Alan Stern, of Southwest Research Institute. “Nothing quite like this has ever been captured in imagery.”
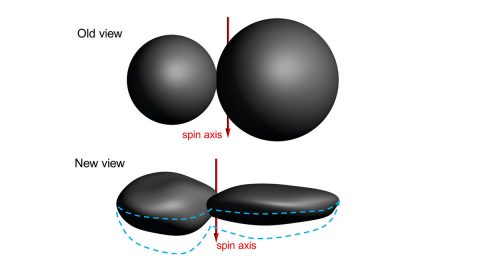
The newly released images also contain important scientific information about the shape of Ultima Thule, which is turning out to be one of the major discoveries from the flyby.
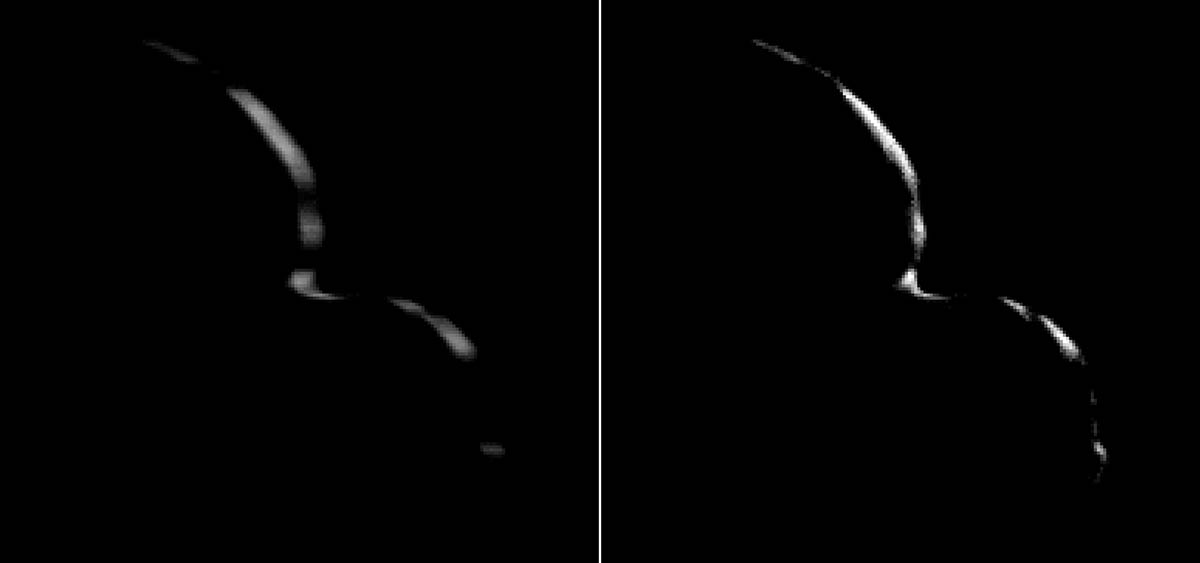
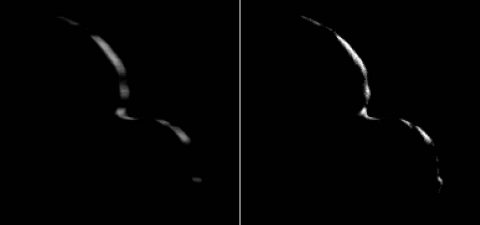
The first close-up images of Ultima Thule – with its two distinct and, apparently, spherical segments – had observers calling it a “snowman.”
However, more analysis of approach images and these new departure images have changed that view, in part by revealing an outline of the portion of the KBO that was not illuminated by the Sun, but could be “traced out” as it blocked the view to background stars.
Stringing 14 of these images into a short departure movie, New Horizons scientists can confirm that the two sections (or “lobes”) of Ultima Thule are not spherical. The larger lobe, nicknamed “Ultima,” more closely resembles a giant pancake and the smaller lobe, nicknamed “Thule,” is shaped like a dented walnut.
The departure images were taken from a different angle than the approach photos and reveal complementary information on Ultima Thule’s shape. The central frame of the sequence was taken on January 1st at 05:42:42 UT (12:42am EST), when New Horizons was 5,494 miles (8,862 kilometers) beyond Ultima Thule, and 4.1 billion miles (6.6 billion kilometers) from Earth.
The object’s illuminated crescent is blurred in the individual frames because a relatively long exposure time was used during this rapid scan to boost the camera’s signal level – but the science team combined and processed the images to remove the blurring and sharpen the thin crescent.
“The shape model we have derived from all of the existing Ultima Thule imagery is remarkably consistent with what we have learned from the new crescent images,” says Simon Porter, a New Horizons co-investigator from the Southwest Research Institute, who leads the shape-modeling effort.
“While the very nature of a fast flyby in some ways limits how well we can determine the true shape of Ultima Thule, the new results clearly show that Ultima and Thule are much flatter than originally believed, and much flatter than expected,” added Hal Weaver, New Horizons project scientist from the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory. “This will undoubtedly motivate new theories of planetesimal formation in the early solar system.”
The images in this sequence will be available on the New Horizons LORRI website this week. Raw images from the camera are posted to the site each Friday.